I’ve noticed PEX plumbing popping up in more homes than ever before, and there’s a good reason for its growing popularity.
This modern plumbing solution has changed how contractors and homeowners approach water line installations, offering advantages that traditional materials simply can’t match.
This modern solution delivers superior flexibility, durability, and cost savings over traditional plumbing materials.
I’ll help you through everything you need to know about this plumbing system, the different types available, how it compares to copper and pvc, installation techniques, and whether it’s the right choice for your project.
What is PEX plumbing?
PEX plumbing refers to a piping system made from cross-linked polyethylene, a durable plastic material that’s revolutionized residential and commercial water distribution.
The “cross-linking” process chemically bonds the polymer chains, creating a pipe that’s flexible yet incredibly strong.
It’s available in three main types of PEX: PEX-A, PEX-b, and PEX-c, each manufactured through different cross-linking methods. Additionally, various PEX connection types enable secure, leak-free installations customized to specific project requirements.
This adaptable material resists scale buildup, withstands extreme temperatures, and can expand slightly when water freezes, reducing the risk of burst pipes.
Types of PEX
To fully understand what PEX plumbing is, you need to know the three main types available, how they’re manufactured, and which one works best for different applications.
1. PEX-A: Peroxide Method

PEX-A, made using the engel method with cross-linking during manufacturing, offers superior expansion memory, allowing it to stretch when water freezes and return to shape without damage.
This type works very well and smoothly with expansion connection types and is ideal for cold climates, though it commands the highest price point.
2. PEX-B: SilaneM
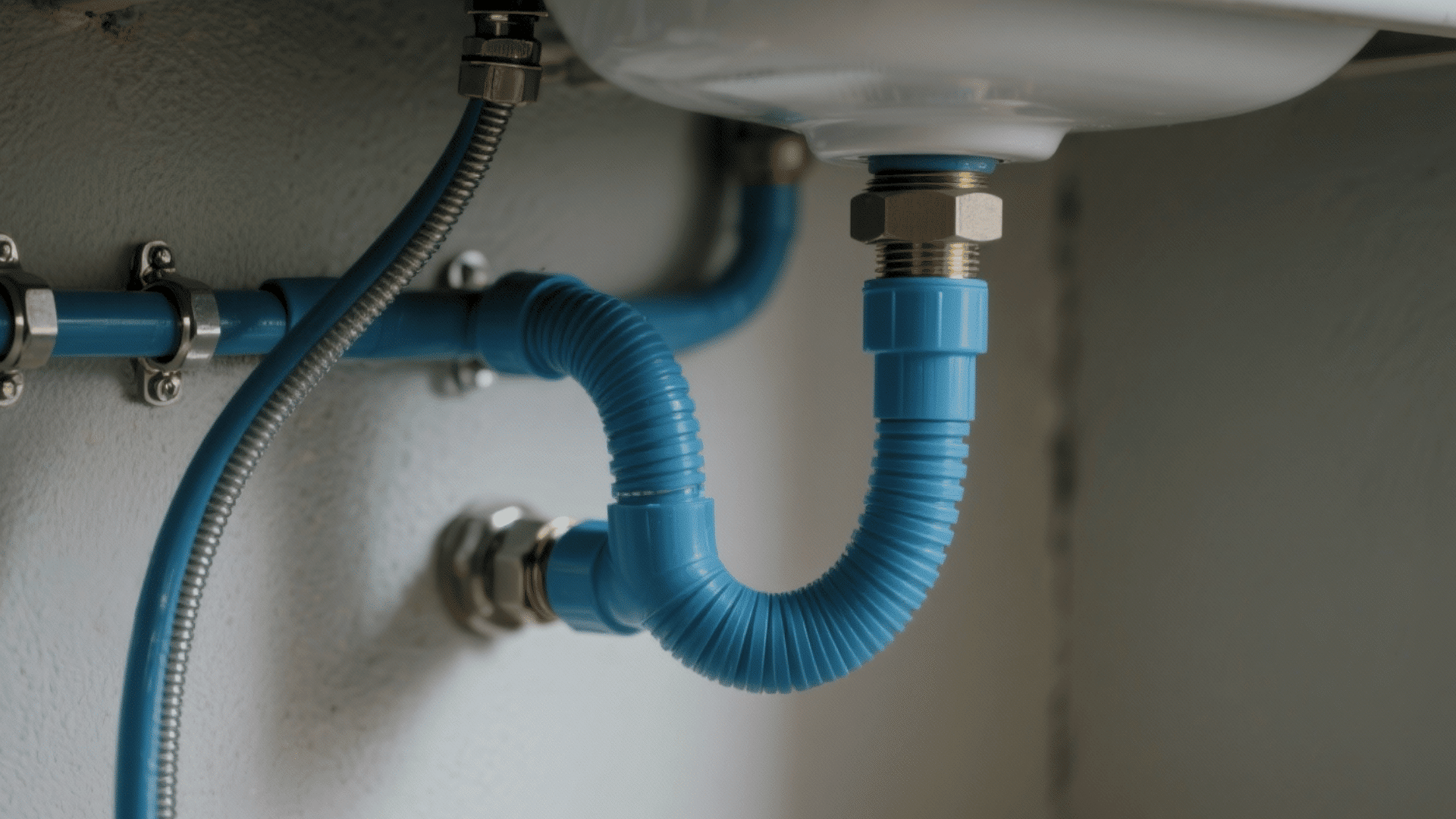
PEX-b represents the middle ground in both performance and cost. It’s crosslinked using a moisture-cure after the extrusion process, resulting in moderate flexibility and excellent chlorine resistance.
This type is compatible with crimp and clamp connection types, making it the most popular choice for residential plumbing installations.
3. PEX-C: Electron Beam Radiation
The most budget-friendly option, PEX-C, undergoes cross-linking after the pipe is formed using electron beam radiation.
Although it’s the stiffest and prone to kinking, it provides reliable performance for straightforward, minimally bent installations. It’s used in manifold systems with long straight runs where flexibility isn’t a priority.
Pros and Cons of PEX Plumbing Systems
PEX plumbing offers impressive benefits, but understanding both its advantages and limitations is essential before choosing it for your project.
| PROS OF PEX PLUMBING | CONS OF PEX PLUMBING |
|---|---|
| PEX installation costs 25–50% less than copper and requires less labor. | PEX breaks down when exposed to sunlight and must be used indoors. |
| It bends easily around corners, reducing the need for many fittings. | It is not suitable for outdoor plumbing or exterior lines. |
| PEX can expand and contract when water freezes without bursting. | Some studies suggest small amounts of chemical leaching may occur. |
| It resists corrosion and mineral buildup, keeping water flow steady. | It cannot be recycled once removed or replaced. |
| PEX is quiet and keeps water hot longer. | It cannot connect directly to water heaters and may attract rodents. |
PEX vs. Copper: Which Material Is Right for Your Home?
When deciding what PEX plumbing offers compared to traditional materials, people face important choices.
PEX costs 25-50% less than copper and installs faster due to flexibility and various PEX connection types available. Copper provides superior heat resistance and doesn’t degrade in uv light, making it ideal for exposed areas.
PEX excels in freeze resistance and corrosion immunity, while copper offers recyclability and proven longevity exceeding 50 years.
For budget-conscious renovations with indoor applications, understanding the different types of PEX helps maximize cost savings, as they are generally considered more effective.
However, copper remains preferable for outdoor installations, maximum durability, and environmental sustainability.
Essential Installation Guidelines on PEX Plumbing
Knowing PEX plumbing involves more than just the material; correct installation is essential for optimal system function. Even seasoned professionals can sometimes make errors that result in leaks, damage, and expensive repairs later.
-
Avoid over-crimping connections and mixing incompatible fittings. Excessive force can damage pipes and restrict water flow, while using the wrong connection types causes system failures. Always verify compatibility before purchasing materials.
-
Protect PEX from UV exposure and heat sources. Direct sunlight can weaken tubing in just a few months, causing brittleness and failure. Never run PEX near recessed lighting or other heat-generating fixtures.
-
Use protective sleeves when running through concrete slabs. PEX needs room to move and protection from abrasion. Running it directly through concrete without sleeves can cause damage and make future repairs nearly impossible.
-
Allow for thermal expansion and contraction. PEX expands more than metal pipes with temperature changes. Avoid over-securing pipes to prevent stress, noise, and potential cracking at connection points.
-
Always pressure test before closing walls. Test at 1.5 times the working pressure for at least 15 minutes. Skipping this step can hide leaks until after construction is complete, leading to expensive repairs.
Following manufacturer guidelines and proper installation ensures your PEX system works reliably for years, safeguarding your investment and maintaining warranty coverage.
Pex Connection Types and Fittings
PEX plumbing offers impressive benefits, but understanding both its advantages and limitations is essential before choosing it for your project.
| CONNECTION TYPE | DESCRIPTION | Compatible PEX Types |
|---|---|---|
| Crimp Connections | Copper or steel rings are crimped around the pipe for a secure, watertight seal. | PEX-A, PEX-B, PEX-C |
| Clamp (Cinch) Connections | Stainless steel rings tightened with a cinch tool for easy, visual sealing. | PEX-A, PEX-B, PEX-C |
| Expansion Connections | Pipe and fitting are expanded, then contract to form a tight bond. | PEX-A |
| Push-Fit Connections | Pipe pushes into a fitting with an internal grab ring—no tools needed. | PEX-A, PEX-B, PEX-C |
| Compression Fittings | Nut and ferrule compress to create a mechanical seal between pipes. | PEX-A, PEX-B, PEX-C |
| Press Connections | Specialized tool presses the fitting onto the pipe for a solid joint. | PEX-A, PEX-B, PEX-C |
| Sweat (Copper) Fittings | Soldered copper joints used to connect PEX to copper lines. | PEX-to-Copper |
Common Applications for PEX Plumbing
Understanding what PEX plumbing is used for helps homeowners and contractors determine when this adaptable material is the best choice.
From residential water distribution to innovative heating solutions, PEX has become the go-to material for diverse plumbing applications across various industries.
1. Residential Water Supply Systems
PEX is ideal for delivering hot and cold water throughout homes, offering flexible routing and reliable performance. The various PEX types make it easy to install in new construction or to replace aging galvanized systems.
Home run manifold systems use PEX plumbing with individual shutoffs for each fixture, making maintenance and repairs simpler than in traditional trunk-and-branch configurations.
2. Remodeling and Retrofitting
When updating older homes, PEX plumbing offers the ability to snake through existing walls without extensive demolition.
Its flexibility allows installation in tight spaces and around obstacles, significantly reducing labor costs and renovation time compared to rigid piping materials. It is a preferred choice for bathroom and kitchen renovations.
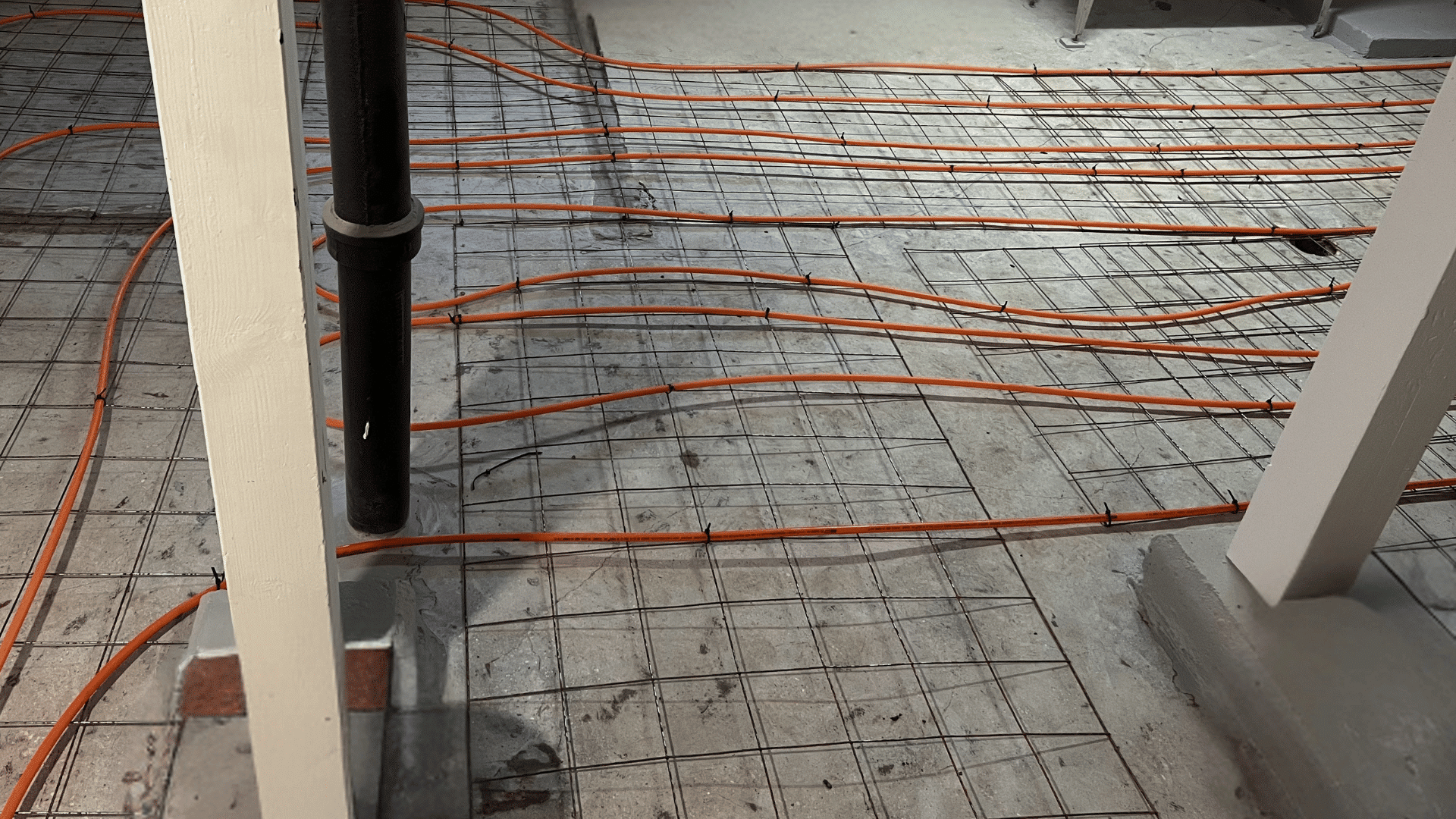
3. Radiant Floor Heating
PEX tubing excels in radiant heating systems, circulating warm water beneath floors to provide efficient, even heat distribution.
The material’s flexibility and resistance to corrosion make it perfect for embedding in concrete slabs or installing between floor joists for comfortable, energy-efficient home heating.
4. Municipal Water Service Lines
Many municipalities now approve PEX for underground water service connections from the street to homes. Its resistance to scale buildup and freeze damage makes it a durable choice for buried applications.
Proper depth and UV protection during installation are important. PEX flexibility reduces the number of connection types, minimizing leak points in buried lines.
5. Snow and Ice Melting Systems
PEX tubing installed beneath driveways, walkways, and outdoor stairs circulates heated water or antifreeze solutions to melt snow and ice.
Commercial properties, hospitals, and residential homes in cold climates increasingly rely on PEX-based hydronic snow melt systems for reliable, automated winter safety.
The Bottom Line
After reviewing what PEX plumbing is, I can say it’s a smart choice for modern homes, offering real advantages over traditional materials despite its limitations, such as UV sensitivity.
Consider PEX for its affordability, durability, and easy setup, and for combining practicality and convenience.
As I’ve outlined, understanding both the strengths and weaknesses of PEX plumbing helps you make an informed decision that’ll serve your home well for years to come.






